For this opportunity I want to provide information about a very good and interesting project in cryptocurrency, this project is called Harmony. So for that, let's see what their vision and mission is in the future and what benefits we get in this project.
Introduction
Since the publication of the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008, the concept of blockchain has spread throughout the world. While decentralized money and applications are well-publicized ideas, design limitations have challenged Bitcoin's core aspirations. The original Bitcoin Blockchain was designed as a peer-to-peer payment system [13] that allows people to transfer value without intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. However, when Bitcoin gained popularity, its performance bottleneck became clear because throughput was limited to ~ 7 transactions per second (TPS), and costs as a payment system became very expensive.
In 2014, Buterin et. Al. [27] proposed a new blockchain infrastructure called Ethereum, which allowed developers to make various types of blockchain applications using "smart contracts." However, Ethereum does not solve scalability problems and, with ~ 15 TPS, fails to support high-throughput applications such as decentralized games or exchanges.
What is Harmony?
Harmony is an open infrastructure high-cost, inexpensive, and inexpensive consensus platform designed to drive a decentralized economy in the future.

Open infrastructure for world data

Global-scale marketplace platform

Activate a decentralized economy and cannot be trusted
Decentralization at Scale

Our goal is to provide scalability and decentralization. The promise of the blockchain is to enable decentralized coordination on a scale but there is no platform that can achieve both. Harmony aims to change it.
Similar to the way Google integrates its search infrastructure vertically, we take a full stack approach to resolving consensus on a large scale. We implement 10x innovations in each layer in consensus algorithms, systems and networks to maximize our network performance while maintaining decentralization. Our end-to-end integration allows us to switch faster and do more aggressive optimization than can be done with a modular approach.
Sharding
The Blockchain sharding as a scalability solution has gained a lot of attention since the end of 2017. Various sharding solutions have been proposed both in industry and in the academic world.
In the industry, Zilliqa [12] is the first publicly-based blockchain shard that claims a throughput of 2,800 TPS. Zilliqa used PoW as an identity registration process (eg Sybil's attack [1] prevention). The Zilliqa network contains a single directory service committee and several shard committees (eg Sharding networks), each containing hundreds of nodes. Transactions are assigned to different fractions and processed separately (eg Fraction of transactions). Blocks generated from all fractions are collected and merged on the directory service committee. Zilliqa is not a sharding country solution because each node must hold the entire blockchain status in order to process transactions.
In academia, publications such as Omniledger [8] and RapidChain [7] have proposed solutions that show sharding countries where each shard holds a subset of the blockchain status. Omniledgers use a multi-party calculation scheme called RandHound [25] to produce safe random numbers, which are used to randomly assign nodes to fractions. The omniledger assumes a slowly adaptive corruption model in which an attacker can damage most nodes in overtime shards. Under such a security model, one shard can eventually be damaged. Omniledgers prevent fraction corruption by remodeling all vertices in fractions at fixed time intervals called periods. RapidChain was built on the Omniledger and proposed the use of the Cuckoo Bound Rules for tampering with nodes without interruption [19].
Distributed Randomness Generation
Various approaches have been proposed to assign nodes into shards such as randomness-based sharding [7,8], location-based sharding [34], and centrally-controlled sharding [35]. Out of all the approaches, randomness-based sharding has been recognized as the most secure solution. In randomness-based sharding, a mutually agreed random number is used to determine the sharding assignment for each node. The random number must have the following properties:
1. Unpredictable: No one should be able to predict the random number before it is generated.
2. Unbiaseable: The process of generating the random number should not be biasable by any participant.
3. Verifiable: The validity of the generated random number should be verifiable by any observer.
4. Scalable: The algorithm of randomness generation should scale to a large number of participants.
Omniledger [8] uses the RandHound protocol [25], which is a lead generation distributed randomization process involving PVSS (Publicly Verified Secret Sharing) and Byzantine Agreement. RandHound is the protocol O (n * c) which divides the participant nodes into groups of 2 with sizes c. This reaches the first three properties above but is very slow to qualify as scalable.
RapidChain [7] takes a simpler approach by allowing each participant to do VSS (Sharing Secret Verification) [22] and use shared secret sharing as a result of randomness. Unfortunately, this protocol is not safe because malicious nodes can send inconsistent parts to various nodes [25]. In addition, RapidChain does not explain how nodes reach consensus on several possible versions of reconstructed randomness.
Blockchain State Sharding
Unlike other state-sharding blockchains [7,8] which adopt the UTXO data model (Unspent Transaction Output), Harmony Sharding State is applied to the account-based data model. Each shard chain contains the status of its own account, and all existing tokens are scattered between all shards.
We treat user accounts and smart contract accounts differently in sharding. User accounts can have multiple balances on different fractions (eg 100 tokens on Shard A and 50 tokens on Shard B). Account users can move balances between shards by issuing cross shard transactions. Smart contract accounts are limited to specific fractions where the contract is made. However, for decentralized applications that require more throughput than can be handled by one fraction, the developer of Dapp (Decentralized Application) can make instantiating multiple instances of the same smart contract in different fractions and allowing each instance to handle a subset of incoming traffic . Note that different examples of the same smart contract do not have the same status, but they can talk to each other through cross-shard communication.
Incentive Model
Consensus Rewards
After the successful commitment of a block, a protocol-defined number of new tokens will be rewarded to all validators who signed the block in proportion to their voting shares. The transactions fees are rewarded to validators similarly.
Slashing Stashing
For any behavior errors detected by the network, a number of tokens at stake will be deducted. For example, if a leader fails to complete the consensus process and triggers the leader's change process, the tokens at stake P will be deducted. If the validator is proven to sign an dish of dishonesty, all votes from their shares under the same fraction will be deducted. This severe punishment is intended to greatly prevent dishonest behavior and make the network as safe as possible. Proof of behavior errors can be two signed blocks that are conflicting. Any validator can submit a transaction to prove the wrong behavior of another validator and if verified, the token that is deducted will be given an award to the authorities.
Stake withdrawal
Long range attack
Proof of stock blockchains, unlike proof of work blockchains, tend to suffer from long-range attacks. This is an attack that utilizes the fact that evidence is based on signatures rather than on resource-intensive tasks. In long-range attacks, the honest validator's private key was stolen long after they were used, and the attacker was able to create a blockchain branch by signing a fake block with those keys. When this happens, the new validator that joins the network has no way to distinguish between the original chain, the legitimate simulation chain and the attacker.
Remote attacks occur in the following two scenarios. The private key can be compromised by a lack of security in the validator, or more generally, in fact, after the validator withdraws the token, he can get financial benefits if the attacker wants to buy his privacy key. In addition, by designing each set of trusted validators to approve transaction blocks that also determine the next set of validators. After enough private keys (ie those who collectively have more than voting rights in a faction) have been compromised, the attacker has total control over 3 2 which is the next validator.
Life at Harmony
We’re on a mission to 1000x the public blockchain. Are you ready to build the next rocketship with a great team? If you’re passionate about a global-scale decentralized future, come join us.
Harmony - for One and All

After working in some of the best technology companies, we together solved the most interesting technical problems. We share an entrepreneurial spirit, and hunger to create important solutions.
Our mission is to bring open consensus to 10 billion people. That is something we will convey to our grandchildren, and we want to have fun making it happen.
A Place to Call Our Own

We’re on a bold mission with a clear target, but the journey to get there matters a lot to us. We want to build a global community that shares our values — empathy, passion, and excellence.
We put in the hours to make things happen, but we also get together for happy hours every now and then. After a long week, we unwind with team yoga. Gym memberships and Macbook Pros are covered, right alongside daily in-house meals. It’s work, the way we think it should be.
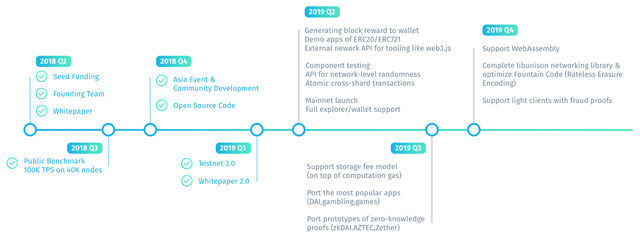
Road Map
Investors

Partners

Conclusion
In addition, the segmented HARMONY Protocol has a positive effect on the DRG distribution system and other network algorithms, reducing the cost of electricity consumption and interacting safely with the entire environment. Which naturally causes a significant reduction in all transaction costs and increases all the benefits of blockchain technology repeatedly. The implementation of strong and high-quality ideas can fundamentally influence the further development of all blockchain technology, because of course every company can use the new HARMONY concept. It doesn't matter whether you want to save data or monetize their business processes. And in both cases, HARMONY will handle the task 100%.
It is also important to note that the creation of this project works with a team of strong and experienced specialists who have previously carried out large-scale projects in companies such as Apple, Google, Amazon and Facebook. That adds unnecessary trust to those who want to get acquainted with the concept of HARMONY in more detail.
Of course, all the most important and complex technical and analytical data from this project are not affected by my damage. Therefore I strongly recommend paying attention to the good proposed technical documentation, which fully reveals all this information.
For more complete information on the Harmony project, see the link below that I have provided.
